Ac Joint Widening Radiology
Acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments may be affected.
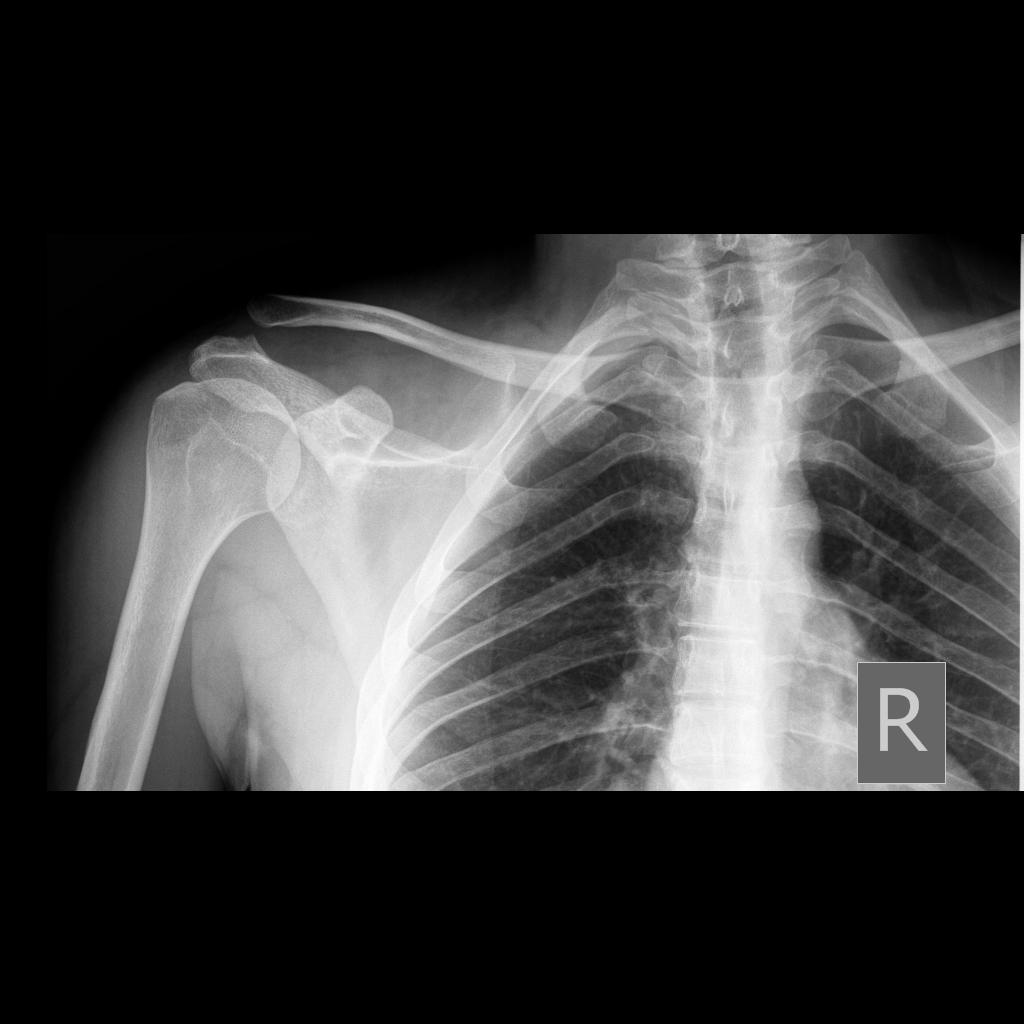
Ac joint widening radiology. 5 8 mm narrower in the elderly. The acromioclavicular joint is a common source of shoulder pain aside from the glenohumeral joint and rotator cuff. Acromiohumeral interval is a useful and reliable measurement on ap shoulder radiographs and when narrowed is indicative of rotator cuff tear or tendinopathy. The acromioclavicular index is helpful to evaluate joint space widening and calculated by dividing the acromioclavicular distance on the contralateral asymptomatic side by that on affected side.
Plain radiograph true ap shoulder r. Symptomatic acromioclavicular joints were present in 23 of patients undergoing shoulder mri acromioclavicular joint dislocation accounts for approximately 12 of all shoulder injuries which is likely an underestimation because minor. Grade 2 involves rupture of the ac ligament or acromioclavicular ligament. Its role in defining pathoanatomy at the acromioclavicular joint.
J surg orthop adv 2004. Features of acromioclavicular joint injury include 6. Grade 1 is a simple sprain to the ac joint with minor damage to the ligament and no separation of bones. Tenderness directly over ac joint with possible deformity ac compression test passively flex arm so it is parallel with ground.
Grade 4 involves posterior displacement or displacement backward. Grade 3 rupture of both ac and cc or coracoclavicular ligaments which often results in an upward displacement of the clavicle bone. The rockwood classification 1998 is the most common classification system in use for acromioclavicular joint injuries 3. Coracoclavicular distance usually 11 13 mm.
These are performed with the patient erect and holding a weight in the arm. Normal measurements do not rule out pathology and must be considered in the context of other findings and the clinical presentation. Evaluation and treatment of acromioclavicular joint injuries. Widening of the acromioclavicular joint.
Widening of ac joint but a normal coracoclavicular distance. In the study by jordan et al. Then passively adduct across body pain suggests ac joint injury. It takes into account not only the acromioclavicular joint itself but also the coracoclavicular ligament the deltoid and trapezius.
This well known 6 type system is a modification of the earlier 3 class classification system described by allman 1967 2 and tossy 1963. Magnetic resonance imaging of the coracoclavicular ligaments. Routine use of stress radiographs is controversial low yield clinical features. 14 mazzocca ad arciero ra bicos j.
From harris and harris radiology of emergency medicine. If the joint is normal then acromioclavicular alignment should remain normal and symmetric. Right and left differ by no more than 2 3 mm. Normal radiographic measurements of the shoulder are important in evaluation of the osseous relationships in plain film radiography.
Ac joint space is usually 5mm. Measurement the shortest distance is measured.