Ac Joint Widening Radiopaedia

Acromioclavicular ac joint injuries definition.
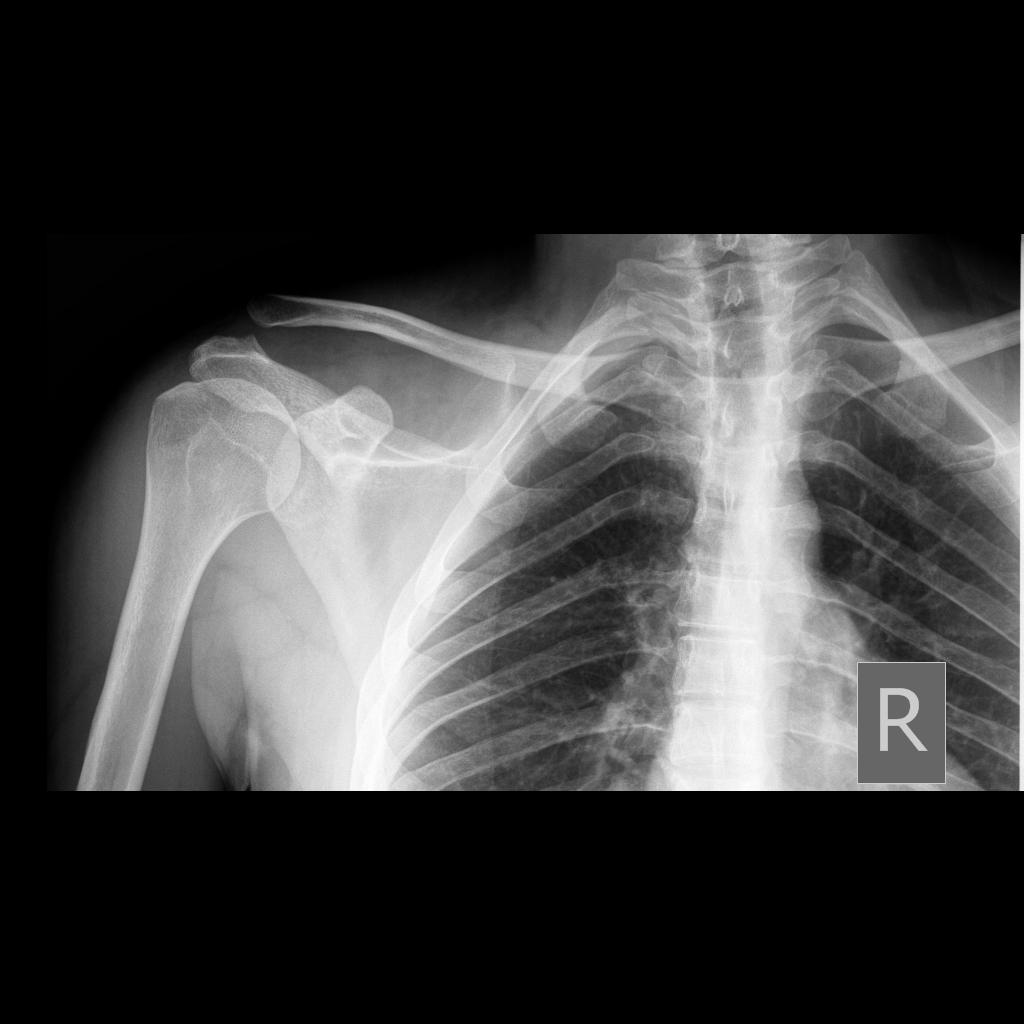
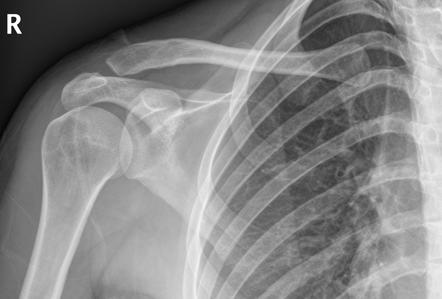
Ac joint widening radiopaedia. The acromioclavicular joint acj is a plane synovial joint diarthrodial joint of the pectoral girdle. May be the only finding in type i injuries. Widening of ac joint but a normal coracoclavicular distance. This well known 6 type system is a modification of the earlier 3 class classification system described by allman 1967 2 and tossy 1963.
Mild asymmetric widening of the ac joint without displacement in a symptomatic patient is consistent with a type i injury. Tenderness directly over ac joint with possible deformity ac compression test passively flex arm so it is parallel with ground. Disruption of both ac and cc ligaments. Grossly enlocated glenohumeral joint.
Acromioclavicular and coracoclavicular ligaments may be affected. Mild asymmetric widening of the ac joint without displacement in a symptomatic patient is consistent with a type i injury. Routine use of stress radiographs is controversial low yield clinical features. 5 8 mm narrower in the elderly.
Then passively adduct across body pain suggests ac joint injury. Gross anatomy the acromioclavicular joint is between the small facet of the convex distal clavicle and flat medial acromion. Dislocation of the left acromioclavicular joint with the clavicle displaced superiorly and widening of the coracoclavicular space 25 mm consistent with coracoclavicular ligament injury rupture. Normal measurements do not rule out pathology and must be considered in the context of other findings and the clinical presentation.
Sprain or tear of the acromioclavicular ac and coracoclavicular cc ligaments. These are performed with the patient erect and holding a weight in the arm. Normal radiographic measurements of the shoulder are important in evaluation of the osseous relationships in plain film radiography. The rockwood classification 1998 is the most common classification system in use for acromioclavicular joint injuries 3.
Stress films may still be required to demonstrate widening of both ac joint and cc space. The findings are in line with a type 3 acromioclavicular joint injury according to the rockwood classification system. Widening of both the ac and cc spaces on routine erect film. Typically a fall on or direct blow to the acromion with the humerus adducted forcing the acromion inferiorly and medially relative to the clavicle.
It takes into account not only the acromioclavicular joint itself but also the coracoclavicular ligament the deltoid and trapezius. Features of acromioclavicular joint injury include 6. If the joint is normal then acromioclavicular alignment should remain normal and symmetric.